Orthopaedic and Fracture Clinic
01246 277271
This placement is part of the general surgery pathway. You will rotate here and to other clinics in surgery including urology. Please click here for Urology


Information about the department
Orthopaedic Out Patients, sometimes referred to as Fracture Clinic or Orthopaedic clinic. This is because we see both elective referrals and trauma referrals. We are part of the Surgical and Orthopaedic division at Chesterfield Royal Hospital.
Patients attending Orthopaedic clinic are referred from their GP/ Muscular Skeletal Services (MSK). Patients attending fracture clinics are referred by the Emergency Department/Minor Injuries Departments/GP/self referral if had an injury whilst on holiday. Patients range from babies up to the very elderly.
The Learning Environment Manager is Rachel Ferreday. The Matron is Angela Innes
Rachel Ferreday - r.ferreday@nhs.net
Student Handbook:

Sickness
If you are sick or going to be absent, please contact the department as soon as possible on 01246 512023 to speak to the nurse in charge. It is also your responsibility to inform your university of any days that you don’t attend placement.
Please be aware that if your sickness is caused by D&V, then it is policy that you must remain off work for 48 hours after your last symptoms.
Hospital emergency contact numbers
2222 – Medical emergency e.g. cardiac arrest
7777- security emergency
2000 - Fire
To bleep a number dial 85 and follow the prompts, enter the three digit bleep number followed by the extension number from which you are dialling.
0 – orator (Voice activated system) state clearly whom you wish to speak
All other regularly used numbers are displayed at the side of the nurses’ station.
The emergency ‘resus’ trolley is in the clinic corridor , just through the first double doors.
Differentiating the staff
Senior Matron – Navy uniform with blue piping
Matron – Navy uniform with red piping
Sisters – Navy uniform with white piping
Staff Nurses – Blue and white stripes
Nurse Associates – Grey with green piping
Healthcare Assistants – Green and white stripes
Physio’s – white tops, blue trousers/piping
OT’s – White tops, green trousers/piping
Receptionist – black top and trousers
Doctors – Navy scrubs
Orthopaedic Consultants
FMA – Mr Ali – soft tissue knee
GRA – Miss Aspinall – Hip & knee – including revisions
JAG – Mr Garcia – Hand and wrist
MWM – Mr Morris – foot and ankle
DIW – Mr Wood – Hip and knee - including revision
SAS – Mr Shahane – upper limb
PMW – Mr Williams – Hip and knee
JDW – Mr Wright – upper limb
APS – Mr Sinha – upper limb
JDM – Mr May – foot and ankle
ESH – Mr Holloway – hip and knee
JVC – Mr Chandrasenen – soft tissue knee
How the department is run
The co-ordinator is usually the most senior nurse on duty for that shift, and they take charge. They delegate duties, oversee activities, co-ordinate the running of the clinics, and sort out staffing problems.
The Health Cares work with the doctors to provide a chaperone for patients and to ensure patients receive all the information required after their appointment. This includes information about coming in for operations, directions to other departments, information about scans including wait times and what to do if they don’t not hear from the imaging department. Health cares also apply splints and slings.
The trained staff take care of patients requiring injections or dressings. They take out sutures/clips and apply splints/slings and record patients body mass index (BMI). They refer patients to community nursing/practice nursing. Sometimes other referrals are necessary such as for safe guarding reasons or because the patient is a venerable adult etc.
Staff in the plaster room treat patients from the clinic and also from ED. They also have patients returning with problems, podiatry patients, ward patients and patients from children’s’ out patient department (The Den).
The clinics have either 1 or 2 doctors assigned to each. This is usually the consultant and their registrar. Between them they see the patients on that sessions list.
General routine
08.30 – staff set up for clinic
09.00 – clinics commence
12.30 – lunchtime, varies on work load
13.30 – clinics recommence
17.00 – clinic close, some exceptions for over running!
Documentation
All patients with an out patient appointment will have a reconciliation form on the front of their notes. This has to be filled in as the information is required to be fed back in to Medway which is the computer system we use in the Trust for appointments. This then generates the income for the appointment. Please take a minute to familiarise yourself with this.
Orthopaedic Information and abbreviations
ACL – Anterior cruciate ligament
Abduction – Moving away from the midline
Adduction – Moving towards the midline
Ankylosing Spondylitis – Rheumatoid degenerative fusing of the vertebrae, resulting in loss of function and position
Arthritis – Inflammation of a joint, usually accompanied by pain and often changes in structure
Arthro – pertaining to a joint
Arthrodesis – Surgical fixation of a joint by fusion
Arthroplasty – An operation to restore or reform a joint to make an artificial joint
Arthroscopy – An operation to look inside a joint with an arthroscope
Arthrotomy – An operation in which a joint is opened surgically.
Aspiration – To drain pus or fluid via a needle
Avascular Necrosis – death of bone cells and bone due to cessation of a blood supply.
Avulsion – Forceful separation or tearing away of two connecting parts
Bradford sling – A sling used to elevate the arm to prevent swelling
Bursa – Sac or cavity composed of synovial membrane containing synovial fluid that serves as a cushioning device between tendon and bone, tendon and ligaments or between two other structures where friction is likely to occur
Bursitis – inflammation of the bursa
Braun frame – a frame used to elevate the leg to prevent swelling
Broad arm sling – a sling used to support the arm
Callus – the osseous material formed between the ends of a structured bone or thickening of a horny layer of skin
Cannulated hip screws – a type of fixation used for hip fractures
Carpal tunnel syndrome – pressure on the median nerve at the point at which it goes through the carpal tunnel of the wrist. It causes soreness, tenderness and weakness of the thumb, index, middle and ring fingers
Cauda Equina – The collection of nerves at the bottom of the spinal cord
Cauda Equina Syndrome – Pressure on the nerves as above
Cellulitis – inflammation of cellular or connective tissue
Charnley wedge – abduction wedge used following hip operations to prevent dislocation
Closed fracture – a fracture without an open skin wound
Colles’ fracture – a fracture of the distal radius in the forearm
Compartment syndrome – increased venous pressure within an enclosed area or compartment that can lead to tissue necrosis if the pressure is not released
CPM – continuous passive movement
CSM – colour, sensation and movement
Debridement – Surgical cutting away of dead tissue or foreign body from a wound
Dislocation – the displacement of any part of bone from its normal position in the joint
Distal – situated away from the centre line of the body
DHS – Dynamic hip screw fixation used for neck of femur fractures
DIP – Distal interphalangeal joint (last finger joint)
DNAR – Do not attempt resuscitation
Effusion – An increase of synovial fluid
EUA – Examination under anaesthetic
Ex-Fix – External fixation to stabilise a fracture with pins attached to an external framework
Fasciotomy – Incision into one or more fascia (covering of muscle) to relieve pressure
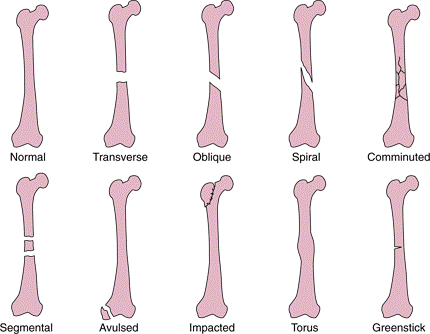
Fracture (#) – a break in the continuity of the bone
Futura Splint – a splint used to support the wrist
FWB – Fully weight bearing
GA – General Anaesthetic
Ganglion – A small cyst – swelling near a joint
Gout – a disease caused by the deposition of sodium waste in and around joints, causing inflammation
Haemoarthrosis – a collection of blood in the joint
Haematoma – a swelling/collection that contains blood
Hyperextension – the extension of a limb beyond its normal position
Iliac crest – Bony ridges at the side of the abdomen on the outer portion of the pelvis
Intracapsular – Within the capsule of a joint, such as a hip or shoulder joint
IM nail – Intramedullary nail, insertion of a metal rod/nail into a fractured bone, see image below.
K-wire – Kirschner wire, a narrow wire used to hold bones together whilst they heal following a fracture or operation
Lateral – to the side
Medial – Inside/to the middle
MUA – Manipulation under anaesthetic
Muscle Atrophy – wearing away of muscle tissue because of disease or paralysis
NBM – Nil by mouth
MP – Metacarpophalangeal joint (joint at the base of the finger)
NOF – Neck of femur
NOH – Neck of humerus
NWB – Non weight bearing
Open fracture – A fracture with the presence of a wound
ORIF – Open reduction and internal fixation
Osteomyelitis – infection in the bone
Osteoporosis – A condition in which bones become soft and spongy
Osteotomy – Surgical opening of bone or cutting through bone
PCA – Patient controlled analgesia
Periprosthetic fracture – a fracture around a prosthetic joint
PIP – Proximal interphalangeal joint (middle finger joint)
Poly sling – A sling used to immobilise the arm
POP – Plaster of Paris
Proximal – Near, close to trunk
PWB – Partial weight bearing
Reduction – Putting a fracture or dislocation back into its correct position
Revision surgery – Surgery to repair/replace an artificial joint
RA – Rheumatoid arthritis
Richard’s Splint – used to immobilise the knee joint
Rotator cuff – Encircling muscles of the shoulder, which permit the shoulder joint to rotate and turn in a circular motion
Sciatica – Pain in the leg from along the sciatic nerve, travelling down the back of the thigh and down the leg
Skin traction - Is used in the temporary treatment of fractures/dislocations to apply traction. It prevents muscle spasms, immobilises the limb and reduces the fracture
Smith’s fracture – A fracture of the distal radius in the forearm
SOF – Shaft of femur
Spinal anaesthetic – an anaesthetic used to give numbness to the lower parts of the body
Sprain – partial tear of a ligament
Stress fracture – A crack or break in a bone due to excessive stretching or pulling. See images below for types of fracture
Subluxation – Partial or incomplete dislocation
TBW – Tension band wiring
Tenotomy – surgical division of a tendon
Thomas splint – used to temporarily stabilise femoral shaft of femur fractures
Thompsons/Hemiarthroplasty – Fixation used for a fractured hip, replaces the head of the femur
THR – Total Hip replacement. Hip prosthesis that replaces both the ball and socket component of the hip
TKR – Total Knee replacement replaces the whole knee joint
Traction – A mechanism for straightening broken bones
TWB – Touch weight bearing
USS – Ultra sound scan
WBAA/T – weight bear as able/tolerated
Infection Control
Please remember to wash hands or use alcohol gel when leaving and entering the department, and all areas.
Bear in mind the 5 moments for hand hygiene:
-
before patient contact
-
before a clean/aseptic procedure
-
after bodily fluid exposure risk
-
after patient contact
-
after contact with patients surroundings
We encourage patients not to attend out patients if they have D & V. We recommend they are 48 hours symptom free.